One of the biggest reasons businesses fail isn’t a bad product—it’s not knowing who to sell it to.
You obviously can’t sell a high-end espresso machine to someone who only drinks instant coffee. No matter how advanced the machine is, they simply aren’t interested because it doesn’t fit their needs or habits.
You’re trying to sell to the wrong people, it doesn’t matter how great your product is; they won’t buy it.
That’s why knowing your target market is so important.
A well-defined target market helps you identify where demand exists, understand customer needs, and create a strategy that resonates with the right market.
Don’t worry if you still haven’t figured out how to identify the target market in your domain. Let’s break it down. We’ll first...
What is a target market for a business?
A target market is a unique group of consumers who share common interests or characteristics and are the ideal fit for purchasing your product or availing your service.
Trying to appeal to everyone can dilute your message and weaken your brand’s impact. As Seth Godin said, “Don’t try to make a product for everybody, because that is a product for nobody.”
Simply put, they are the people your business relies on to generate revenue and operate successfully.
How do you identify your target market?
Follow this guide to identify your target market:
1. Analyze your product or services
First, identify your target market’s core problem your product and service solves—that’s the foundation of an effective products and services section of your business plan. What makes it essential to potential customers? Try to list its unique features and advantages over competitors.
For example, if you’re selling a project management tool—its features might include automation, task tracking, and integrations while its benefits might include increased productivity and reduced errors.
Finally, determine what sets it apart from competitors. Is it more affordable? More user-friendly? Offers better customer support? A clear understanding of these factors will help you attract the right audience and create an effective marketing strategy.
2. Conduct market research
Market research works as the foundation for understanding your target customers, industry trends, and potential competitors.
You can begin by gathering primary data through surveys, focus groups, and direct customer reviews. While the surveys help to identify your target market’s preferences and buying behaviors—the focus groups offer deeper insights into customer pain points and motivations.
Next, analyze secondary data from industry reports, customer reviews, and case studies. Reports from research firms and government databases can highlight the market size, growth potential, and economic trends.
Pay attention to emerging market trends and evolving customer needs. Are there shifts in technology, consumer habits, or regulations affecting demand?
You can use social media and online forums to research and monitor discussions around your industry—the more data you gather, the better you can tailor your product, messaging, and marketing strategy to meet the target customers’ demands effectively.
3. Segment your audience
To identify your target market, audience segmentation plays a crucial role, enabling businesses to tailor their marketing strategies based on distinct consumer characteristics.
To do this effectively, businesses must conduct market analysis to understand customer behavior, preferences, and trends, ensuring their messaging resonates with the right audience.
Segmentation is typically divided into four categories:
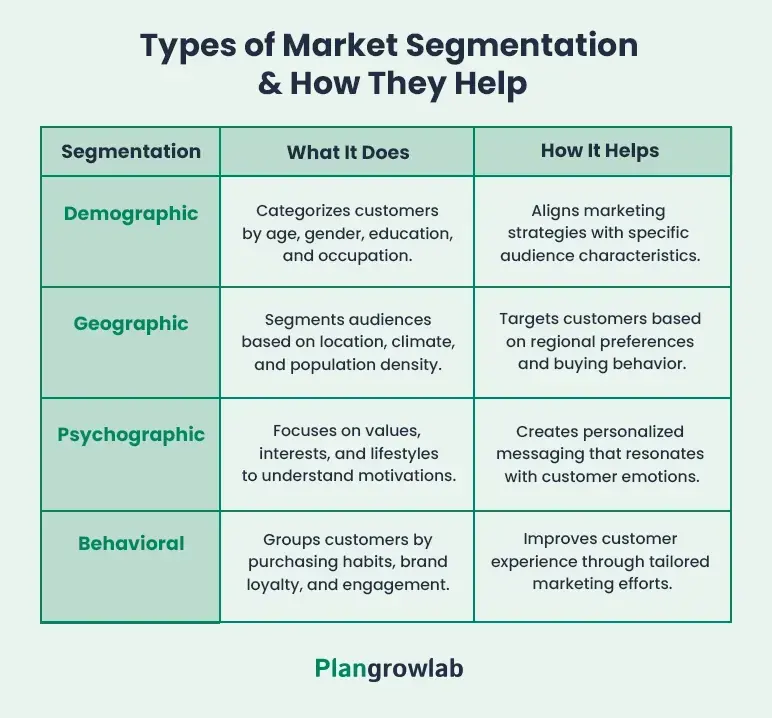
Demographic segmentation
This type of segmentation categorizes customers based on measurable characteristics—such as gender, age, education level, and occupation and significantly influences the purchasing decisions.
For example, a luxury brand might target women aged 30 to 50 years while a budget-friendly brand might focus on college students and young professionals.
Geographic segmentation
This type of segmentation focuses on the customer’s location, including country, region, city, climate, and population density—and impacts purchasing behaviors, lifestyle choices, and product demands.
For example, a winter-wear brand might go heavy on marketing in colder locations while a beachwear brand might target tropical locations.
Psychographic segmentation
This particular type focuses primarily on customers’ values, interests, lifestyles, and personalities. Unlike demographic segmentation which focuses on “who” the customer is—psychographics reveal “why” they buy.
For example, a fitness brand might segment its target audience into groups like “busy professionals” who look for quick workout options or “senior citizens” with joint pain issues who are looking for low-impact workouts to align their marketing efforts accordingly.
Behavioral segmentation
Behavioral segmentation helps you divide your customer base based on their purchasing patterns, brand interactions, and product usage.
Thinking about how you can segregate your customers based on their behaviors? Well, here are the factors that help you do that:
- Purchase frequency: Helps you understand whether your customers are one-time buyers or repeat purchasers.
- Brand loyalty: Explains whether your target audience sticks to one brand or frequently switches.
- Price sensitivity: Shows whether your customers prioritize costs over quality and helps determine if they are willing to pay for premium products.
- Engagement level: Helps you understand the engagement level of the audience through emails, social media, or loyalty programs.
4. Create a buyer persona
A buyer persona is a semi-fictional representation of your target customers based on market research and real customer data that helps you understand your audience and identify your target market on a deeper level.
Begin with analyzing the demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioral data that you collected to create customer profiles. Then, move on to identify common patterns in your customer base—such as age, income level, location, lifestyle preferences, and buying habits.
A well-crafted buyer persona includes:
- Name and background: Give your persona a realistic name and give a brief background that summarizes their lifestyle, job role, and personal details to make them more relatable.
- Demographics: Include important demographic details such as—age, gender, income, education, marital status, and location.
- Pain points: Identify the challenges and frustrations they face that your product or service can solve.
- Buying behaviors: Understand their purchasing habits and decision-making process—like purchasing frequency, preferred mode of shopping, most-used platforms, and more.
- Preferred communication channels: Find out how your audience prefers to engage and communicate—do they prefer emails, social media, or direct messaging? Knowing this helps tailor your marketing strategies effectively.
- Goals: Understand what they aim to achieve that’s relevant to your product or service and how you can help to achieve them.

5. Analyze competitors’ target markets
Analyzing your competitors’ target markets helps you understand what works, what doesn’t, and where you can stand out.
Start by identifying direct and indirect competitors. Direct competitors offer similar products or services, while indirect competitors serve the same needs differently.
Check their website, social media, and customer reviews to see who they’re targeting. Pay attention to their branding, messaging, and advertising—do they focus on affordability, luxury, convenience, or innovation?
Look at how they position themselves in the market. Some brands cater to high-income professionals who prioritize premium quality, while others appeal to budget-conscious shoppers looking for value. Competitor pricing, customer engagement, and product features will give clues about their ideal audience.
Now, find gaps where you can differentiate. Are they ignoring a specific segment? If competitors focus on luxury customers, you could target budget-conscious shoppers who still want high-quality products but at a more affordable price.
Once you’ve identified gaps, decide how to position your brand:
| Positioning strategy | How it works | Key advantages |
|---|---|---|
| Compete directly | Offer a better product, price, or service to attract budget-conscious customers. | Appeals to cost-sensitive customers. |
| Partially overlap | Target a similar audience but focus on unique benefits to stand out. | Helps create brand loyalty and differentiates from competitors without direct conflict. |
| Find a unique niche | Cater to an underserved market, such as affordable sustainable options in a luxury-dominated space. | Can establish a strong brand identity in a new segment. |
The ideal way to approach this is not just to copy what competitors do—but to find market gaps and serve unmet needs.
6. Test and refine your target market
Even if you have a clear idea of your audience, things change. Market trends shift, competitors step up their game, and customer needs evolve. That’s why refining your approach is key.
Start by running small test campaigns—try different messaging, offers, and ad formats to see what sticks. Use tools like Facebook Ads, Google Ads, and email marketing to target different groups and compare performance.
Keep an eye on Google Analytics, social media insights, and customer feedback. Look at who’s visiting your website, where they drop off, and what content gets the most attention.
Do not forget customer feedback. Customer feedback is gold. Read reviews, send out surveys, or talk to your audience on social media. Are they looking for a cheaper option? A missing feature? A better user experience? Their input helps you fine-tune your marketing and product to fit their needs better.
Once you’ve got enough data, make adjustments. If one group engages but doesn’t buy, maybe your pricing needs work. Keep testing, keep refining, and you’ll zero in on the perfect approach to identify your target market.
How to find a target market for a new product?
Finding a target market for a brand-new product requires a strategic mix of research, testing, and adaptation. Since there’s no direct competitor data—you’ll need to be flexible and rely on real-world feedback.
While the fundamental steps of market research still apply, here are some of the strategies that will answer your question—how to find a target market for a new product.
1. Start with the problem
For a brand-new product, your first step isn’t to find a target market. Here you need to define the problem your product or service solves. Since people aren’t searching for your product yet, identify the pain points or inefficiencies it addresses.
Ask yourself: Who’d benefit most from this solution? Then, look for people who are actively seeking alternatives or are frustrated with current solutions.
For example, if you create a smart wearable that helps people fall asleep faster—your target audience might include individuals with insomnia, frequent travelers, or people struggling with stress-related sleep issues.
2. Identify adjacent market segments
Even if your product is entirely new—it likely serves a need that’s already being addressed in some way. Since direct competitors don’t exist, look at adjacent markets and analyze similar products that serve your audience differently.
In this case, since this smart sleep wearable has no direct competitors—the potential indirect competitors might include sleep aid apps, sleep sound generators, and sleep-inducing teas.
3. Test multiple market hypothesis
Since no established customer base exists, don’t assume a single target market. Instead, create multiple market hypotheses—potential groups that may be interested in your product and test them.
For smart sleep wearables, possible buyer personas may include overworked employees who struggle to unwind, travelers suffering from jet lag, individuals interested in improving sleep naturally, and more.
4. Monitor search trends
If people don’t know your product exists yet, they won’t be searching for it directly—but they’re searching for solutions. For the smart sleep wearable, they are probably searching for ways to sleep better.
You can use Google Trends, and SEO tools and explore if the search for terms like “sleep-tracking devices” or “smart sleeping aids” are increasing. If it’s increasing, this validates that people are already looking for solutions in this space.
5. Adapt as you learn
Your first target market might not be the right one—so, be prepared to pivot.
Let’s say for the smart sleep wearable, it may happen that the tech-enthusiast audience doesn’t respond well but health-conscious consumers do—shift your messaging toward wellness instead of gadgets.
Tips to precisely define your target market
Here are some tips to help you understand how to define the target market in a business plan:
1. Don’t target everyone
Trying to attract everyone dilutes your strategy and makes your marketing strategies ineffective. Instead, focus on a specific group with shared needs and preferences.
For example, a sleep wearable isn’t for everyone to focus on groups that actively struggle with sleep—such as stressed professionals, frequent travelers, or people with insomnia.
2. Break down the target market
Market segmentation helps break down your total audience into manageable groups based on demographics, psychographics, or behavior.
For instance, instead of targeting “everyone who wants better sleep,” refine it to working professionals aged 30-50 who suffer from sleep deprivation due to stress.
3. Segment your audience based on niche
Beyond age and income, explore psychographics (lifestyle, interests) and decision-making styles.
For the smart wearable, some may prioritize scientifically-backed sleep solutions, while others want natural, drug-free options. You can also target wellness-conscious individuals or parents of newborns who do not get enough sleep.
4. Align your business identity
Your company should align with what you do best and preach.
If your expertise lies in health technology, position your brand as a science-backed solution. If you prefer a holistic wellness approach, target users looking for natural, non-invasive sleep aids.
The bottom line
Now that you know how important it is to define your target market, it’s time to put that knowledge into action. Instead of casting a wide net and hoping for the best, zero in on the people who actually need your product.
A well-defined target market helps you allocate resources wisely, craft marketing strategies that speak directly to the right people, and avoid the costly mistake of reaching the wrong audience.
But identifying the right market isn’t always easy—especially for a brand-new product. That’s where expert guidance comes in.
A business plan consultant specializes in helping entrepreneurs pinpoint their ideal market, validate demand, and develop strategies that drive real growth. Whether you're just starting out or refining your approach—a solid business plan makes all the difference.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the key factors when defining a target market?
There are several key factors—including demographics (age, gender, income, location), psychographics (lifestyle, interests, values), behavioral patterns (buying habits, brand loyalty), and pain points (problems your product solves).
Can your business have more than one target market?
Yes, many businesses serve multiple target markets. However, it’s essential to tailor messaging and marketing strategies to each group rather than using a one-size-fits-all approach.
How to create an ideal buyer persona?
A buyer persona is a detailed representation of your ideal customer. Start by gathering data from market research, customer surveys, and competitor analysis and then define the key characteristics like age, profession, income, lifestyle, pain points, and purchasing behavior.
How do you test your target market?
Testing your target market involves validating your assumptions before scaling your business. You can:
- Run small ad campaigns on social media targeting different audience segments.
- Analyze engagement and conversion rates to see which group responds best.
- Use A/B testing to compare different messaging and product positioning.
- Collect feedback from early adopters through surveys, beta testing, or product trials.

